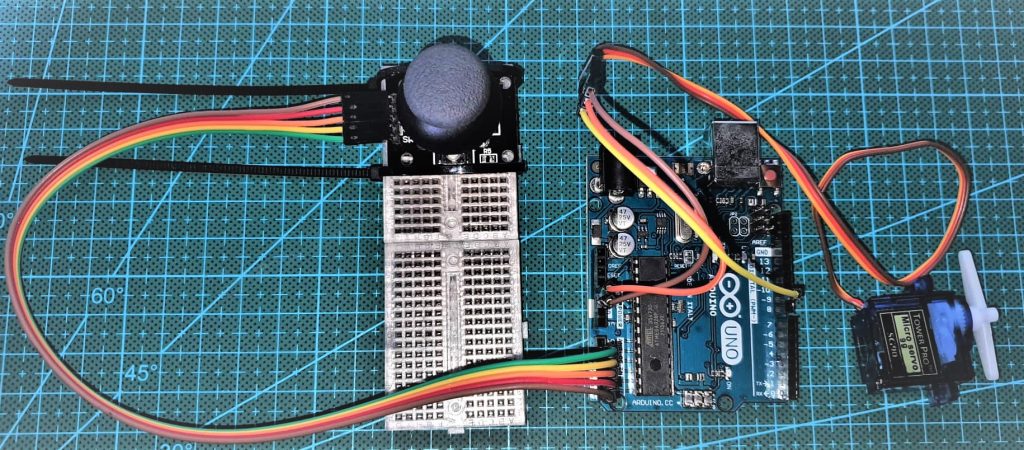
One of the neat projects you can run with Arduino is incorporating a joystick to work in tandem with a servo motor. This allows for various applications, such as a servo-mounted camera and a robotic arm. For our simplest example, the only library that needs to be included is the < Servo.h> library.
What You Will Need
First, we need to list down what we need. We only need a few things to get us started in this quick example.
- Arduino Uno
- Analog Joystick
- SG90 Servo
- Jumper Wires
- Breadboard (optional)
Wiring Diagram
Next, let’s wire up the components. All five pins of the analog joystick can be connected to A1 through A5 (GND, 5V, VRx, VRy, SW, respectively). However, only GND, 5V, and VRx will be used in this example. As for the SG90 Servo, the GND and 5V connect to the respective pins on the Arduino Uno. In this example, we connected the servo signal line to digital pin 9. Below are the wiring diagram and wiring table.
| Arduino Uno | Analog Joystick | Arduino Uno | SG90 Servo |
| A1 | SW | GND | GND |
| A2 | VRy | 5V | Vcc |
| A3 | VRx | D9 | Signal |
| A4 | 5V | ||
| A5 | GND |
Right two columns: Arduino to Servo

Programming
Finally, we create the code to upload to the Arduino. As mentioned a while ago, the only library we need for this activity is . Below is the code that was used for this activity.
#include <Servo.h>
#define SERVO_PIN 9
#define GROUND_JOY_PIN A5
#define VOUT_JOY_PIN A4
#define XJOY_PIN A3
#define YJOY_PIN A2
#define SJOY_PIN A1
int servo_val;
Servo myservo ;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(VOUT_JOY_PIN, OUTPUT) ; //pin A4 shall be used as output
pinMode(GROUND_JOY_PIN, OUTPUT) ; //pin A5 shall be used as output
digitalWrite(VOUT_JOY_PIN, HIGH) ; //set pin A4 to high (+5V)
digitalWrite(GROUND_JOY_PIN,LOW) ; //set pin A5 to low (ground)
myservo.attach(9);
}
void loop()
{
delay(200);
int joystickXVal = analogRead(XJOY_PIN) ;
servo_val=map(joystickXVal, 4, 1017, 10, 175);
Serial.print(joystickXVal);
Serial.println(" = input from joystick");
Serial.print(servo_val);
Serial.println(" = output to servo");
Serial.println() ;
myservo.write(servo_val);
}Serial Monitor
Lastly, for additional information, the serial monitor will print the reading that it gets from the joystick. The value indicated in the “output to servo” is the value from the joystick that has gone through the map() function and then pushed to the Servo.




